Metallic photos of the sun by renowned photographer Greg Piepol bring together the best of art and science. Buy one or a whole set. They make a stellar gift. | | | X-FLARE: For days, giant sunspot AR1515 has looked capable of producing a really strong explosion. On July 6th it finally did. Yesterday, the sunspot's magnetic canopy erupted, producing a brief but potent X1.1-class solar flare. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory recorded the extreme ultraviolet flash: 
The explosion hurled a CME into space. According to this movie from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, the cloud appears to be heading south and away from Earth. However, we cannot yet rule out a glancing blow to our planet on July 8th or 9th. Stay tuned for further analysis. Look at the CME movie one more time. The speckles near the end are caused by energetic protons accelerated by the flare. Guided toward Earth by solar magnetic fields, the protons are peppering Earth-orbiting satellites, causing "snow" in imaging systems and posing a slim threat for single-event upsets (computer glitches). X-flare alerts: text, voice. Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery INCOMING CME: On July 4th, sunspot AR1515 hurled at least four minor CMEs into space. Most flew south of the ecliptic plane (the orbital plane of the planets), on track to miss everything. One of them, however, appears to be heading toward Earth. Click to view an animated forecast track of the incoming cloud: 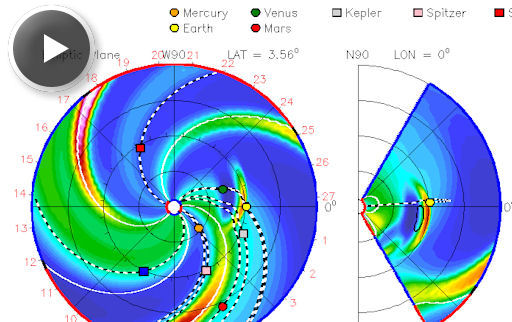
According to analysts at the Goddard Space Weather Lab, who prepared the forecast, the cloud will reach Earth on July 7th around 0600 UT. High-latitude sky watchers should be alert for auroras on that date. Aurora alerts: text, voice.
Realtime Noctilucent Cloud Photo Gallery
[previous years: 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2011] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On July 7, 2012 there were 1320 potentially hazardous asteroids. Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Mag. | Size | | 2012 MY2 | Jun 29 | 1.3 LD | -- | 24 m | | 2003 KU2 | Jul 15 | 40.2 LD | -- | 1.3 km | | 2004 EW9 | Jul 16 | 46.8 LD | -- | 2.1 km | | 2002 AM31 | Jul 22 | 13.7 LD | -- | 1.0 km | | 37655 Illapa | Aug 12 | 37 LD | -- | 1.2 km | | 2000 ET70 | Aug 21 | 58.5 LD | -- | 1.1 km | | 1998 TU3 | Aug 25 | 49.2 LD | -- | 4.9 km | | 2009 AV | Aug 26 | 62.8 LD | -- | 1.1 km | | 1998 UO1 | Oct 4 | 60.1 LD | -- | 2.1 km | Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather | | 
