Learn to photograph Northern Lights like a pro. Sign up for Peter Rosen's Aurora Photo Courses in Abisko National Park, winner of the TripAdvisor Certificate of Excellence Award 2015. | | |
(ALMOST) NO CHANCE OF FLARES: Solar activity is very low. Not one of the small sunspots currently dotting the solar disk is actively flaring. As a result, the sun's X-ray output has flatlined. NOAA forecasters say the odds of a strong solar flare today are no more than 1%. Aurora alerts: text or voice
SOLAR WIND SPARKS BRIGHT AURORAS: For the second day in a row, a stream of solar wind is buffeting Earth's magnetic field. This has caused G2-class geomagnetic storms and bright auroras over parts of the USA and Europe. "Last night was epic," reports Ruslan Merzlyakov, who sends this picture from Nykøbing Mors, Denmark:
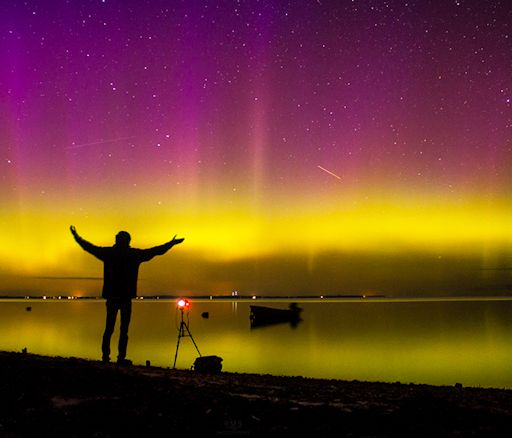

"These were the brightest auroras I have ever seen in my life," he says. "Thank you, spaceweather, for the alert!" (You're welcome.)
Elsewhere in Europe, colorful lights appeared over Sweden, Norway, Scotland, and Finland, while electrical currents surged through the soils of the Lofoten archipelago. Northern Lights were seen in the USA as far south as Maine, Massachusetts, Wisconsin, New York, and South Dakota.
More auroras may be in the offing. NOAA forecasters estimate a 55% of geomagnetic storms on Sept. 8th as the solar wind continues to blow. Aurora alerts: text or voice
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
WILDFIRE AT THE EDGE OF SPACE: On Sept. 6th, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus launched a space weather balloon equipped with radiation sensors. It was a regular flight, part of their weekly program to monitor cosmic rays in the atmosphere. En route to the stratosphere, cameras on the payload looked back and observed an enormous wildfire. This is the view from 109,600 feet:

The massive plume of smoke, pictured right, is coming from the Rough Fire, an 86,000 acre inferno raging through King's Canyon National Park in central California. Smoke from the fire is choking much of the Sierra Nevada mountain range where our space weather balloons are launched.
We've been using balloons and Geiger tubes to monitor cosmic radiation for the past two years. This particular balloon flight attempted something new: using microbes to measure radiation. Five different strains of yeast were flown alongside conventional radiation sensors to calibrate the microbes' response to cosmic rays. This kind of experiment could lead to new and improved techniques for measuring the biological effectiveness of high-altitude radiation.
HEY THANKS! The students of Earth to Sky Calculus wish to thank Dr. Mark Casafrancisco, whose generous donation of $500 made this research flight possible. Here is his business card floating in the stratosphere:
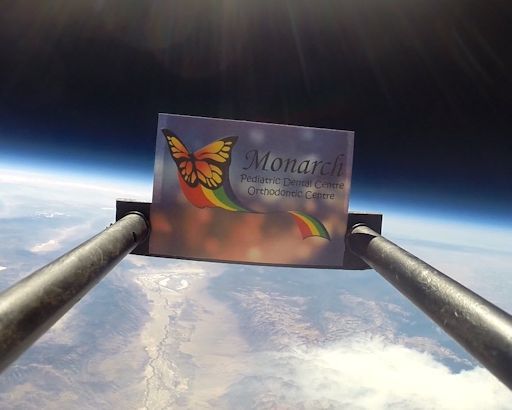

"Sending my business card to space not only allows me to support your student research program, but also shows how proud I am of our out-of-this-world family of stellar staff and pediatric dentists at Monarch Pediatric Dental Centre in Vancouver, BC, Canada!" he says.
Readers, if you would like to sponsor a research flight and see your photo at the edge of space, please contact Dr. Tony Phillips to make arrangements.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
RED AIRGLOW OVER CHILE: On Sept. 1st, astrophotographer Yuri Beletsky hiked into the Atacama Desert of Chile for a deep exposure of the Milky Way. He got that and much more. "There was a stunning display of red airglow," he says. It surrounded the Milky Way like a celestial bulls-eye:

Airglow is aurora-like phenomenon caused by chemical reactions in the upper atmosphere. Human eyes seldom notice the faint glow, but It can be photographed on almost any clear dark night, anywhere in the world.
The curious thing about Beletsky's photo is not the presence of airglow, but rather its color--red. Airglow is usually green, the color of light from oxygen atoms some 90 km to 100 km above Earth's surface. Where does the red come from? Instead of oxygen, OH can produce the required color. These neutral molecules (not to be confused with the OH- ion found in aqueous solutions) exist in a thin layer 85 km high where gravity waves impress the red glow with a dramatic rippling structure.
"It was a truly special night," says Beletsky. "Pure tranquility."
Realtime Sprite Photo Gallery
Realtime NLC Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Sep. 8, 2015, the network reported 13 fireballs.
(10 sporadics, 2 September epsilon Perseids, 1 alpha Aurigid)
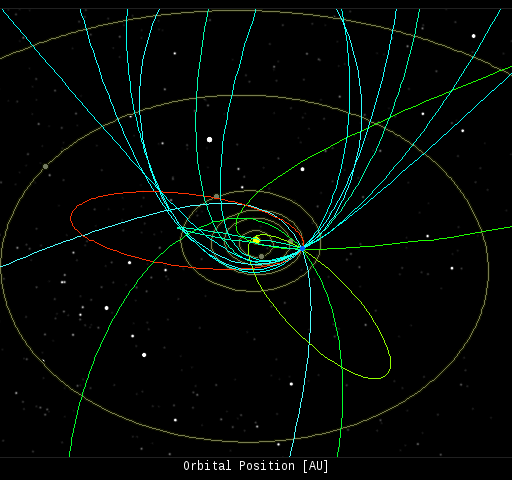
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On September 8, 2015 there were potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |
| | Web-based high school science course with free enrollment |

