When is the best time to see auroras? Where is the best place to go? And how do you photograph them? These questions and more are answered in a new book, Northern Lights - a Guide, by Pal Brekke & Fredrik Broms. | | | SMALL ASTEROID HITS EARTH: Newly-discovered asteroid 2014 AA hit Earth's atmosphere on Jan. 2nd. The space rock, about the size of a small car, disintegrated over the Atlantic Ocean about 3,000 km east of Caracas, Venezuela. Infrasound records interpreted by Peter Brown of the University of Western Ontario suggest an impact energy between 500 and 1,000 tons of TNT. That's a lot of dynamite; nevertheless, in cosmic terms this was a relatively minor impact that did no damage to our planet. [more] BIG SUNSPOT, CHANCE OF FLARES: Sunspot AR1944, which emerged over the sun's eastern limb on Jan. 1st, is big and potentially dangerous. The complex region contains more than a dozen dark cores, and the leading spot is big enough to swallow two planet Earths all by itself. AR1944 is so large, sky watchers on Earth are beginning to notice it as a blemish on the solar disk at sunset: 
"This was my first sunset shot of the year," says photographer Raymund Sarmiento of Quezon City, the Philippines. "AR1944 is circled. That sunspot has the potential to disrupt transmission/reception of radio signals on the foreground antenna." Indeed, the sunspot has a 'beta-gamma' magnetic field that harbors energy for strong eruptions. NOAA forecasters estimate a 75% for M-flares and 30% for X-flares on Jan. 3rd. The effect of any flares today will be mitigated by the fact that the sunspot is not yet directly facing Earth. However, even an off-center blast from this behemoth could produce radio blackouts and geomagnetic activity. Stay tuned for developments. Solar flare alerts: text, voice. 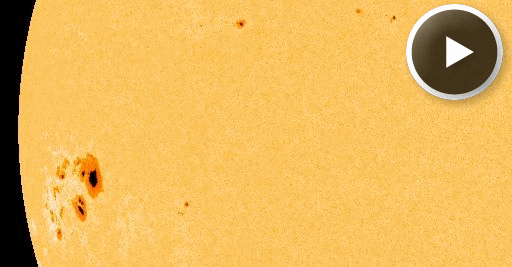
Above: A movie from SDO shows AR1944 emerging on Jan. 1-3.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery GREEN VORTEX OVER SWEDEN: For the second day in a row, a solar wind stream is buffeting Earth's magnetic field, sparking intermittant geomagnetic storms and auroras around the Arctic Circle. Last night, Northern Lights tour guide Chad Blakley photographed a luminous green vortex over Sweden's Abisko National Park: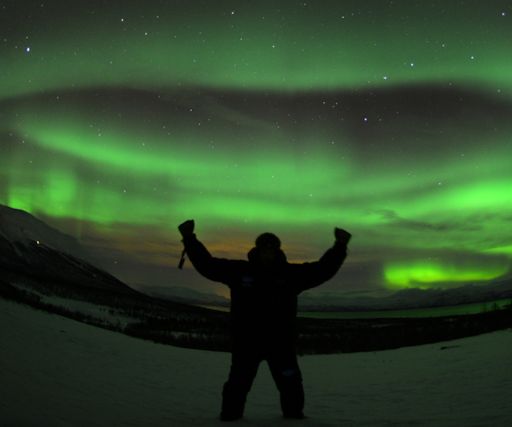 
"Tonight was one of those nights that makes being an aurora photographer the best job in the world," says Blakley. "The lights started around 5:00 PM and continued well into the night. I had the pleasure of spending the evening with Peter Richards, a representative of National Geographic student photography expeditions. At one point during our night under the stars I heard him say that the display was the most amazing thing he had ever seen in his life - I couldn't agree more!" NOAA forecasters estimate a 25% chance of more polar geomagnetic storms on Jan. 3rd as the solar wind continues to blow. Aurora alerts: text, voice. Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Realtime Venus Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Jan. 3, 2014, the network reported 27 fireballs.
(14 sporadics, 13 Quadrantids) 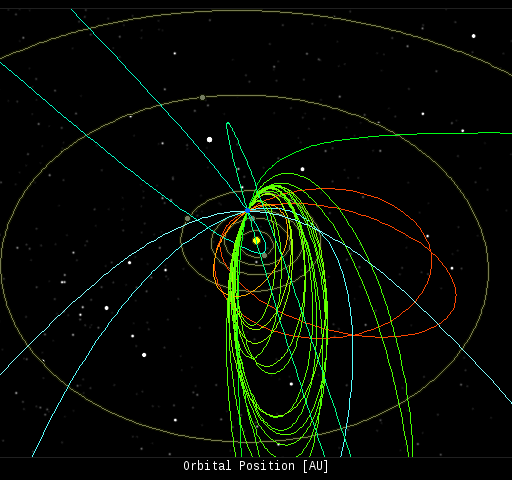
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] On Jan. 2, 2014, the network reported 6 fireballs.
(6 sporadics) 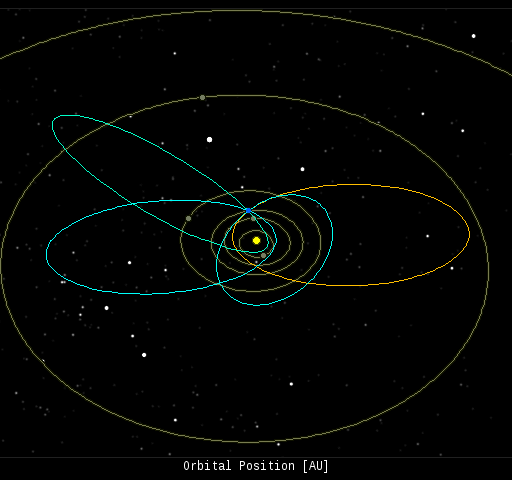
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On January 3, 2014 there were potentially hazardous asteroids. Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather | | 
