| Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) |
| 2019 WR4 | 2019-Dec-31 | 11.7 LD | 4.2 | 21 |
| 2019 YK | 2020-Jan-01 | 14.1 LD | 7.3 | 53 |
| 2020 AX | 2020-Jan-01 | 19.4 LD | 7.3 | 21 |
| 2020 AC | 2020-Jan-02 | 3.4 LD | 5.8 | 17 |
| 2019 YL6 | 2020-Jan-02 | 20 LD | 4.8 | 29 |
| 2020 AD | 2020-Jan-02 | 2.3 LD | 15.6 | 13 |
| 2019 YH2 | 2020-Jan-02 | 7.4 LD | 14.3 | 81 |
| 2020 AP1 | 2020-Jan-02 | 0.9 LD | 5.6 | 4 |
| 2019 AE3 | 2020-Jan-02 | 4.9 LD | 8.2 | 13 |
| 2020 AC1 | 2020-Jan-02 | 2.1 LD | 6.2 | 7 |
| 2020 AN1 | 2020-Jan-04 | 2.6 LD | 11.8 | 25 |
| 2019 YB4 | 2020-Jan-04 | 3.3 LD | 6.1 | 16 |
| 2020 AW | 2020-Jan-06 | 4.8 LD | 4.3 | 7 |
| 2019 YT3 | 2020-Jan-07 | 13.2 LD | 7.4 | 26 |
| 2020 AJ1 | 2020-Jan-07 | 13.5 LD | 22.1 | 78 |
| 2020 AR1 | 2020-Jan-08 | 6.9 LD | 9.6 | 13 |
| 2019 YV | 2020-Jan-10 | 17.3 LD | 4.5 | 68 |
| 2019 YF4 | 2020-Jan-10 | 3.7 LD | 2.9 | 15 |
| 2019 UO | 2020-Jan-10 | 11.8 LD | 9.4 | 331 |
| 2019 WC5 | 2020-Jan-11 | 6.4 LD | 13 | 109 |
| 2019 YV5 | 2020-Jan-11 | 16.8 LD | 13.9 | 48 |
| 2020 AO1 | 2020-Jan-12 | 8.5 LD | 17.8 | 66 |
| 2020 AE | 2020-Jan-13 | 11.7 LD | 6.8 | 26 |
| 2020 AE1 | 2020-Jan-13 | 6.6 LD | 4.2 | 12 |
| 2020 AO | 2020-Jan-14 | 9.4 LD | 19.5 | 50 |
| 2011 EP51 | 2020-Jan-15 | 19.6 LD | 7.1 | 32 |
| 2017 RZ15 | 2020-Jan-15 | 12.1 LD | 7.4 | 14 |
| 2019 YD3 | 2020-Jan-16 | 6.9 LD | 4.8 | 22 |
| 2010 AE30 | 2020-Jan-17 | 11.9 LD | 12.3 | 68 |
| 2019 YG1 | 2020-Jan-17 | 17.5 LD | 4.5 | 32 |
| 2019 YQ3 | 2020-Jan-17 | 18.2 LD | 3.1 | 18 |
| 2020 AD1 | 2020-Jan-17 | 9.1 LD | 4.5 | 19 |
| 2020 AH1 | 2020-Jan-18 | 15.9 LD | 8 | 45 |
| 2009 BH2 | 2020-Jan-18 | 14.6 LD | 17.9 | 118 |
| 2019 YA5 | 2020-Jan-19 | 11.7 LD | 5.2 | 24 |
| 2020 AQ1 | 2020-Jan-20 | 10.3 LD | 27.4 | 138 |
| 2013 DU | 2020-Jan-20 | 14.9 LD | 6.4 | 59 |
| 2019 TF2 | 2020-Jan-23 | 16.2 LD | 1.6 | 18 |
| 2018 BM5 | 2020-Jan-23 | 13.1 LD | 8.6 | 12 |
| 2018 AL12 | 2020-Jan-30 | 18.2 LD | 17.7 | 39 |
| 2017 AE5 | 2020-Feb-01 | 13.6 LD | 9 | 135 |
| 2018 BU1 | 2020-Feb-02 | 19.4 LD | 10 | 41 |
| 163373 | 2020-Feb-15 | 15.1 LD | 15.2 | 589 |
| 2018 CW2 | 2020-Feb-17 | 6 LD | 10.2 | 28 |
| 2019 BE5 | 2020-Feb-20 | 13.9 LD | 14.8 | 34 |
| 2011 DR | 2020-Feb-23 | 14.7 LD | 5.8 | 25 |
| 2016 CO246 | 2020-Feb-23 | 18.4 LD | 5.9 | 23 |
| 2012 DS30 | 2020-Feb-26 | 12.3 LD | 5.4 | 22 |
| 2015 BK509 | 2020-Feb-28 | 18.3 LD | 12.5 | 118 |
| 2017 BM123 | 2020-Mar-01 | 10.5 LD | 8.1 | 65 |
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
SOMETHING NEW! We have developed a new predictive model of aviation radiation. It's called E-RAD--short for Empirical RADiation model. We are constantly flying radiation sensors onboard airplanes over the US and and around the world, so far collecting more than 22,000 gps-tagged radiation measurements. Using this unique dataset, we can predict the dosage on any flight over the USA with an error no worse than 15%.
E-RAD lets us do something new: Every day we monitor approximately 1400 flights criss-crossing the 10 busiest routes in the continental USA. Typically, this includes more than 80,000 passengers per day. E-RAD calculates the radiation exposure for every single flight.
The Hot Flights Table is a daily summary of these calculations. It shows the 5 charter flights with the highest dose rates; the 5 commercial flights with the highest dose rates; 5 commercial flights with near-average dose rates; and the 5 commercial flights with the lowest dose rates. Passengers typically experience dose rates that are 20 to 70 times higher than natural radiation at sea level.
To measure radiation on airplanes, we use the same sensors we fly to the stratosphere onboard Earth to Sky Calculus cosmic ray balloons: neutron bubble chambers and X-ray/gamma-ray Geiger tubes sensitive to energies between 10 keV and 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
Column definitions: (1) The flight number; (2) The maximum dose rate during the flight, expressed in units of natural radiation at sea level; (3) The maximum altitude of the plane in feet above sea level; (4) Departure city; (5) Arrival city; (6) Duration of the flight.
SPACE WEATHER BALLOON DATA: Approximately once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with radiation sensors that detect cosmic rays, a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. Cosmic rays can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Furthermore, there are studies ( #1, #2, #3, #4) linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the general population. Our latest measurements show that cosmic rays are intensifying, with an increase of more than 18% since 2015:
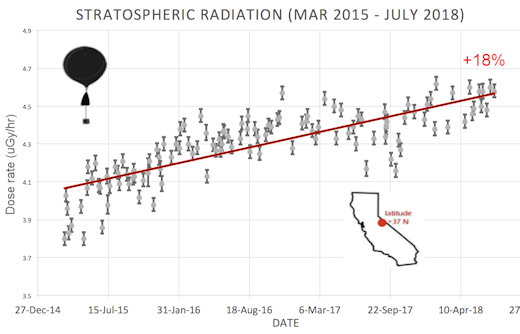
The data points in the graph above correspond to the peak of the Reneger-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Reneger and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today.
En route to the stratosphere, our sensors also pass through aviation altitudes:
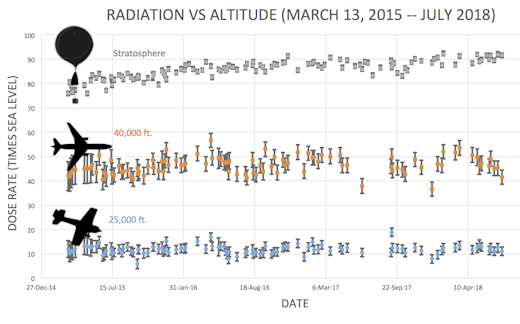
In this plot, dose rates are expessed as multiples of sea level. For instance, we see that boarding a plane that flies at 25,000 feet exposes passengers to dose rates ~10x higher than sea level. At 40,000 feet, the multiplier is closer to 50x.
The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
Why are cosmic rays intensifying? The main reason is the sun. Solar storm clouds such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays when they pass by Earth. During Solar Maximum, CMEs are abundant and cosmic rays are held at bay. Now, however, the solar cycle is swinging toward Solar Minimum, allowing cosmic rays to return. Another reason could be the weakening of Earth's magnetic field, which helps protect us from deep-space radiation.
| | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |
 | To find reviews of new online casino sites in the UK try The Casino DB where there are hundreds of online casino reviews complete with bonuses and ratings. Get a bonus when playing at a new casino in the UK. The Genie got you covered! Looking for a new online casino? Try Casimpo the new site dedicated to making online casino simple and easy for all. |
| | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! |
| | | | | | |

