 The space shuttle is orbiting Earth. Would you like to see it? Sign up for Spaceweather PHONE.
The space shuttle is orbiting Earth. Would you like to see it? Sign up for Spaceweather PHONE.
DISINTEGRATING SUNSPOT: Giant sunspot 898 continues to break apart. Observers now count at least four fragments cloven by arcs of seething, magnetized plasma, as shown in this picture from Stanescu Octavian of Timisoara, Romania. The spot will vanish a few days from now when it goes behind the sun's western limb. See it while you can.
AURORA WARNING: On July 6th, an M2-class explosion near sunspot 898 hurled a massive coronal mass ejection (CME) into space. The cloud is not coming directly toward Earth, but it could deliver a glancing blow to our planet's magnetic field on July 7th or 8th. Sky watchers, be alert for auroras!
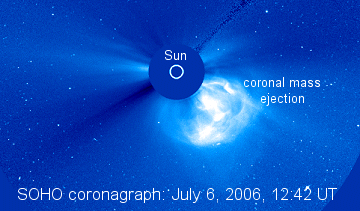
Coronal mass ejections are billion-ton clouds of gas expelled from the sun by explosions in the solar atmosphere. Next to the blinding sun, CMEs are very difficult to see, but the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is able to do it. Coronagraphs onboard SOHO use opaque disks to block the sun's glare, revealing nearby stars, planets, comets and billion-ton clouds of gas.
RED vs. RED JR: The long-awaited collision between Jupiter's Great Red Spot and Red Jr is underway. So far, both storms are holding their own:

Photo credit: Christopher Go of Cebu City, the Philippines.
Closest approach "should happen late next week," says Philippine astronomer Christopher Go who has been tracking the storms's convergence. Although no one knows what will happen, researchers have offered some possibilities: Storm bands may peel off, forming new turbulent curly-cues. Red Jr might lose its red color, turning white. Or the two storms could pass unscathed and unaltered.
See for yourself: Jupiter is an easy target for backyard telescopes. It appears in the evening sky, popping out of the twilight about halfway up the southern sky: finder chart.

