|
SpaceWeather.com |
Global
Notes: This is a northern hemisphere shower. |
|
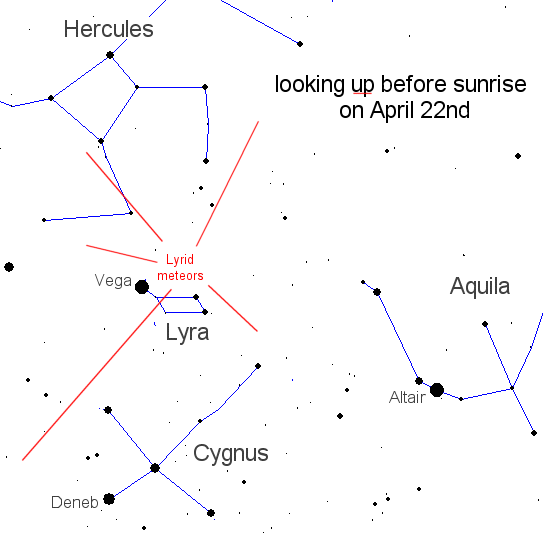
Every year in late April Earth passes through the dusty tail of Comet Thatcher (C/1861 G1), and the encounter causes a meteor shower--the Lyrids. This year the shower peaks on Friday morning, April 22nd. The best time to look, no matter where you live, is during the hours before dawn. Forecasters expect 10 to 20 meteors per hour visible from dark-sky sites. Lyrid meteors appear to stream from the bright star Vega in the constellation Lyra:
In fact, Lyrids have nothing to do with Vega. The true source of the shower is Comet Thatcher. Every year in April, Earth plows through Thatcher's drawn-out dusty tail. Flakes of comet dust, most no bigger than grains of sand, strike Earth's atmosphere traveling 49 km/s (110,000 mph) and disintegrate as streaks of light--meteors! Lyrid meteors are typically as bright as the stars in the Big Dipper, which is to say of middling brightness. But some are more intense, even brighter than Venus. These "Lyrid fireballs" cast shadows for a split second and leave behind smokey debris trails that linger for minutes. Occasionally, the shower intensifies. Most years in April there are no more than 5 to 20 meteors per hour during the shower's peak. But sometimes, when Earth glides through an unusually dense clump of comet debris, the rate increases. Sky watchers in 1982, for instance, counted 90 Lyrids per hour. An even more impressive outburst was documented in 1803 by a journalist in Richmond, Virginia, who wrote:
What will the Lyrids do this year? The only way to know for sure is to go outside and look. Experienced meteor watchers suggest the following viewing strategy: Dress warmly. Bring a reclining chair, or spread a thick blanket over a flat spot of ground. Lie down and look up somewhat toward the east. Meteors can appear in any part of the sky, although their trails will tend to point back toward the radiant--i.e., toward Vega. Vega is a brilliant blue-white star about three times wider than our Sun and 25 light years away. About 14,000 years ago Vega was the North Star. Earth's spin axis wanders: Now it points at Polaris, then it pointed at Vega. You might have seen Vega in Carl Sagan's movie Contact. It was the source of alien radio transmissions to Earth.
|