When is the best time to see auroras? Where is the best place to go? And how do you photograph them? These questions and more are answered in a new book, Northern Lights - a Guide, by Pal Brekke & Fredrik Broms. | | | INCOMING CME, GLANCING BLOW POSSIBLE: Earth could receive a glancing blow from a CME on July 13th. It comes from a magnetic filament that erupted from the sun's northern hemisphere on July 9th and hurled part of itself into space. Minor geomagnetic storms are possible when the CME arrives. Follow the action @spaceweatherman. THREE SUPERMOONS IN A ROW: Today's full Moon is a perigee "supermoon," as much as 14% closer and 30% brighter than other full moons of the year. John Stetson photographed the swollen orb setting over Sebago Lake, Maine, this morning just minutes after sunrise: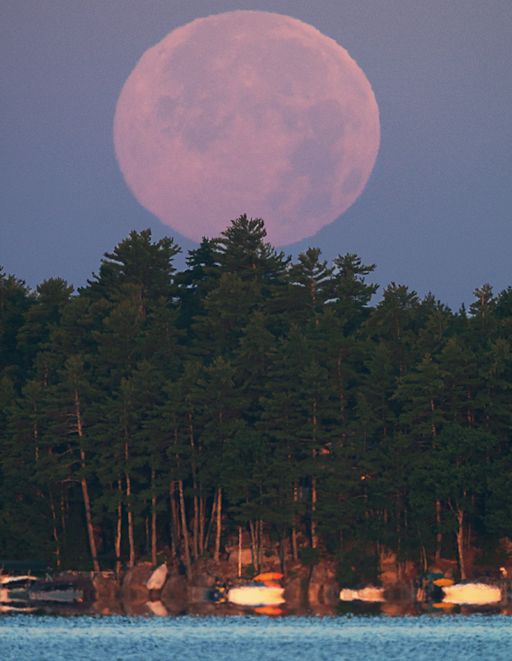 
"An inferior mirage appears in the foreground where the lake meets the shoreline," points out Stetson. Thiis was just the first of three supermooons in a row. Two more are coming on August 10th and September 9th. Get the full story and a video from Science@NASA. Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery NOCTILUCENT CLOUDS: Last night another outbreak of noctilucent clouds appeared over Europe. Photographer Peter Rosén of Stockholm, Sweden, stitched together 24 exposures taken with a fisheye lens to produce a "Little Planet" projection: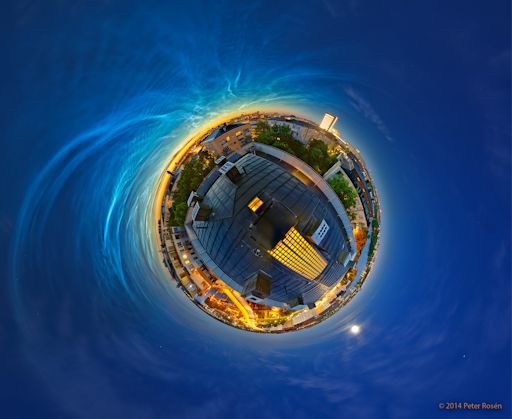 
"The NLC display last night was just incredible and covered half of the sky with electric blue filaments," says Rosen. "Normaly the Moon would have stolen the show, but a night like this it looked quite lonely on the southern horizon." NLCs are Earth's highest clouds. Seeded by "meteor smoke," they form at the edge of space 83 km above Earth's surface. When sunlight hits the tiny ice crystals that make up these clouds, they glow electric blue. In the northern hemisphere, July is the best month to see them. NLCs appear during summer because that is when water molecules are wafted up from the lower atmosphere to mix with the meteor smoke. That is also, ironically, when the upper atmosphere is coldest, allowing the ice crystals of NLCs to form. The natural habitat of noctilucent clouds is the Arctic Circle. In recent years, however, they have spread to lower latitudes with sightings as far south as Utah and Colorado. This will likely happen in 2014 as well. Observing tips: Look west 30 to 60 minutes after sunset when the Sun has dipped 6o to 16o below the horizon. If you see blue-white tendrils zig-zagging across the sky, you may have spotted a noctilucent cloud. Realtime NLC Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Jul. 12, 2014, the network reported 11 fireballs.
( 11 sporadics) 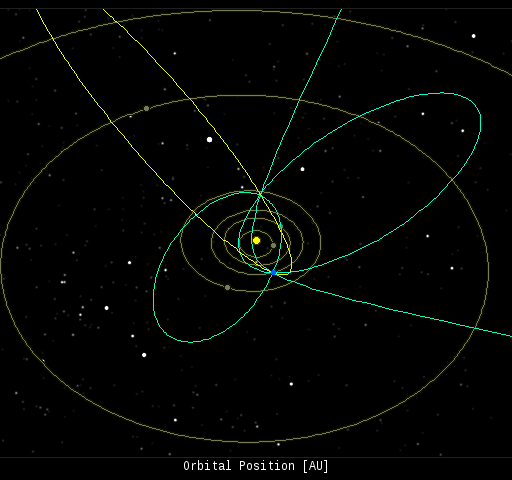 In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On July 12, 2014 there were 1490 potentially hazardous asteroids. Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather | | 
