 | | | Switch to: Europe, USA, New Zealand, Antarctica Credit: NOAA/Ovation  Planetary K-index Planetary K-index
Now: Kp= 2 quiet
24-hr max: Kp= 2 quiet
explanation | more data
Interplanetary Mag. Field
Btotal: 3.4 nT
Bz: 2.3 nT north
more data: ACE, DSCOVR
Updated: Today at 2347 UT  Coronal Holes: 12 Aug 18 Coronal Holes: 12 Aug 18 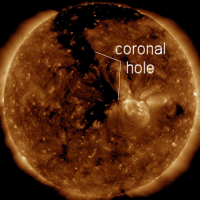
Solar wind flowing from this coronal hole could reach Earth on Aug.16-17. Credit: SDO/AIA  Noctilucent Clouds The season for noctilucent clouds in he northern hemisphere is underway. Check here daily for the latest images from NASA's AIM spacecraft. Switch view: Europe, USA, Asia, Polar Updated at: 08-12-2018 15:55:03 Noctilucent Clouds The season for noctilucent clouds in he northern hemisphere is underway. Check here daily for the latest images from NASA's AIM spacecraft. Switch view: Europe, USA, Asia, Polar Updated at: 08-12-2018 15:55:03  SPACE WEATHER
NOAA Forecasts | | Updated at: 2018 Aug 12 2200 UTC FLARE | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | CLASS M | 01 % | 01 % | CLASS X | 01 % | 01 % |  Geomagnetic Storms: Geomagnetic Storms:
Probabilities for significant disturbances in Earth's magnetic field are given for three activity levels: active, minor storm, severe storm Updated at: 2018 Aug 12 2200 UTC Mid-latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 15 % | 10 % | MINOR | 05 % | 01 % | SEVERE | 01 % | 01 % | High latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 15 % | 15 % | MINOR | 25 % | 20 % | SEVERE | 20 % | 10 % | | | |  | | | | | | | | | | | All-inclusive Northern Lights trips in Tromsø, Norway. Small groups, big experiences! Highly qualified guides ensure unique and unforgettable adventures with a personal touch. Visit Explore the Arctic | | | THE PERSEID METEOR SHOWER IS INTENSIFYING: Perseid meteor rates are swiftly climbing as Earth moves deeper into the debris zone of comet 109P/Swift-Tuttle. Forecasters expect as many as 100 meteors per hour when the shower peaks on Aug. 12th and 13th. The sky is getting so busy that astrophotographers are having trouble keeping meteors out of their exposures: 
"On Saturday night, Aug 10th, a Perseid meteor streaked by my framed image of M27, the Dumbbell Nebula," says photographer Ric Babcock of San Juan Bautista, CA. The Perseid meteor shower is always good, but this year it is extra-good. The Moon is nearly New during the shower's peak, providing a velvety-dark backdrop for the display. The best time to look is during the hours before sunrise on Sunday, August 12th, and again on Monday, August 13th. At those times, the shower's radiant will be high in the sky, spewing meteors in all directions: 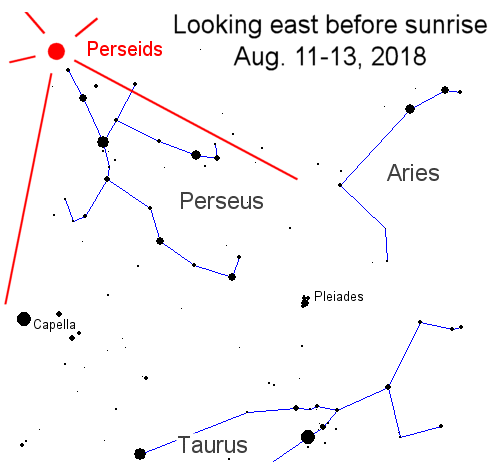
For best results, get away from city lights. Dress warmly, lie down on a blanket in a safe, dark place, and look up. Perseids can appear in any part of the sky, although all of their tails will point back toward the radiant in the constellation Perseus. Realtime Meteor Photo Gallery
ARCTIC AURORA SEASON BEGINS: "This is it! The new aurora season is here," reports Thomas Kast of Oulu, Finland, near the Arctic Circle. "On Aug. 12th, I went to a little marina near Oulu to catch some Perseids and noctilucent clouds (NLCs). Suddenly this weak green arc appeared behind the NLCs." 
"I'm so thrilled to have seen auroras finally again after four months of summer sunlight," he says. "It's like the first time all over again. Pure magic." As aurora season begins, noctilucent cloud season refuses to end. Normally in August, summertime noctilucent clouds (NLCs) begin to fade as weather conditions in the mesosphere disfavor the formation of meteor-seeded ice crystals. This August, however, NLCs are going strong, with the clouds being reported to Spaceweather.com four times as often as during the same period in 2017. Previous studies have shown that NLCs sometimes intensify during solar minimum. Perhaps that is what is happening now. If so, electric-blue and aurora-green may be mixing again in the nights ahead. Stay tuned. Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery FLY ME TO THE MOONSTONE: Are you looking for a far-out gift? Nothing says "I love you" like a moonstone from the edge of space. On Jan 27th, the students of Earth to Sky Calculus flew this moonstone wrapped in a hand-crafted sterling silver Celtic love knot 35.1 km (115,158 feet) above Earth's surface: 
You can have it for $179.95. The students are selling these pendants to support their cosmic ray ballooning program. Each one comes with a greeting card showing the item in flight and telling the story of its journey to the edge of space. All sales support the Earth to Sky Calculus cosmic ray ballooning program and hands-on STEM research. Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All sales support hands-on STEM education
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Realtime Noctilucent Cloud Photo Gallery Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Aug. 12, 2018, the network reported 105 fireballs.
(55 Perseids, 47 sporadics, 2 gamma Eridanids, 1)  In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On August 12, 2018 there were 1912 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 | Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) | | 2018 PM10 | 2018-Aug-10 | 3.2 LD | 7.8 | 14 | | 2018 PD20 | 2018-Aug-10 | 0.1 LD | 12 | 12 | | 2018 PL10 | 2018-Aug-18 | 19.4 LD | 12.6 | 135 | | 2018 PK9 | 2018-Aug-22 | 17 LD | 9 | 31 | | 2018 PW7 | 2018-Aug-23 | 11.4 LD | 10.6 | 44 | | 2018 PR9 | 2018-Aug-24 | 18.1 LD | 14 | 46 | | 2018 LQ2 | 2018-Aug-27 | 9.4 LD | 1.5 | 39 | | 2016 GK135 | 2018-Aug-28 | 16.8 LD | 2.8 | 9 | | 2016 NF23 | 2018-Aug-29 | 13.3 LD | 9 | 93 | | 1998 SD9 | 2018-Aug-29 | 4.2 LD | 10.7 | 51 | | 2018 DE1 | 2018-Aug-30 | 15.2 LD | 6.5 | 28 | | 2001 RQ17 | 2018-Sep-02 | 19.3 LD | 8.3 | 107 | | 2015 FP118 | 2018-Sep-03 | 12.3 LD | 9.8 | 490 | | 2017 SL16 | 2018-Sep-20 | 8.5 LD | 6.4 | 25 | | 2018 EB | 2018-Oct-07 | 15.5 LD | 15.1 | 155 | Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
Readers, thank you for your patience while we continue to develop this new section of Spaceweather.com. We've been working to streamline our data reduction, allowing us to post results from balloon flights much more rapidly, and we have developed a new data product, shown here: 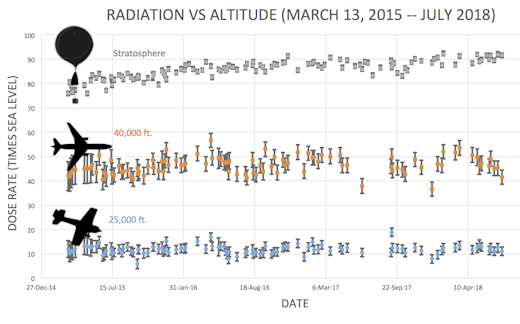
This plot displays radiation measurements not only in the stratosphere, but also at aviation altitudes. Dose rates are expessed as multiples of sea level. For instance, we see that boarding a plane that flies at 25,000 feet exposes passengers to dose rates ~10x higher than sea level. At 40,000 feet, the multiplier is closer to 50x. These measurements are made by our usual cosmic ray payload as it passes through aviation altitudes en route to the stratosphere over California. What is this all about? Approximately once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with radiation sensors that detect cosmic rays, a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. Cosmic rays can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Furthermore, there are studies ( #1, #2, #3, #4) linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the general population. Our latest measurements show that cosmic rays are intensifying, with an increase of more than 13% since 2015: 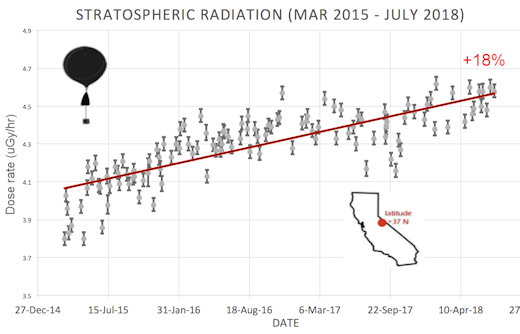
Why are cosmic rays intensifying? The main reason is the sun. Solar storm clouds such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays when they pass by Earth. During Solar Maximum, CMEs are abundant and cosmic rays are held at bay. Now, however, the solar cycle is swinging toward Solar Minimum, allowing cosmic rays to return. Another reason could be the weakening of Earth's magnetic field, which helps protect us from deep-space radiation. The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners. The data points in the graph above correspond to the peak of the Reneger-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Reneger and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather |  | If you are a Youtuber and want to buy real Youtube views than try out Buyrealsocial.com for the best results possible! |  | To find reviews of new online casino sites in the UK try The Casino DB where there are hundreds of online casino reviews complete with bonuses and ratings. | | | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! | | | | | | | | |  | |  |   | ©2017 Spaceweather.com. All rights reserved. This site is penned daily by Dr. Tony Phillips. | |

