When is the best time to see auroras? Where is the best place to go? And how do you photograph them? These questions and more are answered in a new book, Northern Lights - a Guide, by Pal Brekke & Fredrik Broms. | | |
DECREASING CHANCE OF FLARES: NOAA forecasters have downgraded the chance of X-flares on Jan. 14th to 15% as giant sunspot AR1944 rotates off the solar disk. The odds on Jan. 15th are even lower: 1%. A quiet spell appears to be in the offing. Solar flare alerts: text, voice.
FROZEN BUBBLES: Science teacher Tom Wagner of Waterloo, Iowa, is an avid photographer of snowflakes. Over the years he has discovered a great way to catch large flakes in mid-air: "I blow a soap bubble and allow the snowflake to land on it," he explains. Once the snowflake is properly corralled, the photography is relatively easy.
Last week when the Polar Vortex descended over Iowa, Wagner went outdoors to capture some more snowflakes. Just one problem: It was so cold outside, the soap bubbles themselves froze:
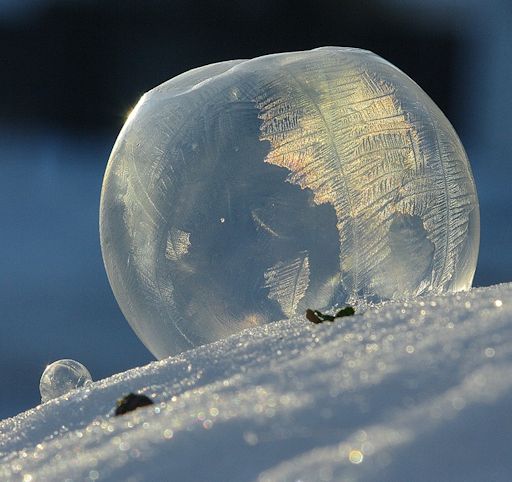

"I made a decision to photograph these frozen bubbles on the snow," says Wagner. "The sun was 20 minutes from setting so I had to act fast. Most of the bubbles popped when they landed but with some practice I discovered a technique that resulted in quite a few remaining intact."
"After a few pictures at home I hurried over to a nearby cemetery where there was still several more minutes of direct sunlight. The men digging nearby must have wondered what I was doing blowing little bubbles onto the snow then lying next to them with my camera in hand. Having the sun in the immediate background illuminated the fern-like crystals growing within the curved bubble skin."
More of Wagner's cold weather photography may be found on his Facebook page.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
JUPITER AND THE MOON: When the sun goes down tonight, step outside and look east. The waxing full Moon is having a close encounter with Jupiter. Stojan Stojanovski sends this picture of the meeting from Velmej-Ohrid, Macedonia:
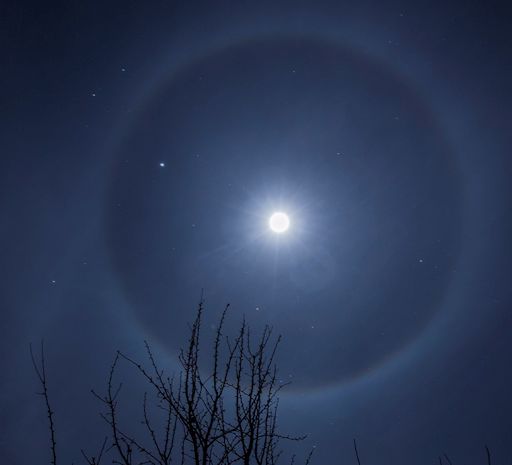

In Stojanovski's photo, the Moon has circumscribed Jupiter inside a luminous ring. It's a 22o halo, caused by ice crystals in high cirrus clouds. Lunar ice halos are most often seen when the Moon is high and bright. With Jupiter so close to the bulls-eye, tonight is a great time to look!
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
SPACE WEATHER BALLOON UPDATE: The payload of a space weather balloon launched Jan. 8th by the students of Earth to Sky Calculus has been recovered from its landing site in Death Valley National Park. The purpose of the flight was to study a solar radiation storm in progress at the time of the launch. Analyzing the data will take a few days. Meanwhile, here is the view from the stratosphere:
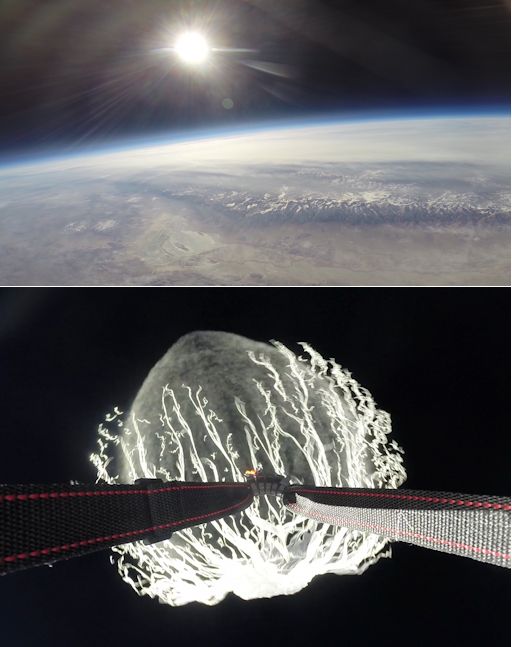

These pictures were taken by a pair of Hero3+ cameras looking out of the payload capsule. The upper frame shows the Sierra Nevada mountain range, unusually brown for this time of year as California endures a historic drought. The lower frame captures the balloon popping at an altitude of approximately 100,000 feet. Click on each frame for a closer look. The landscape shot was made using the Hero3+'s new "superview mode"--a favorite of snowboarders and now, for the first time, balloonists!
Update: Here are some more images from tthe flight: A sundog over Owens Valley, Death Valley from the Edge of Space, Coyote Flats.
In addition to cameras, the payload contained an x-ray/gamma-ray dosimeter, a GPS altimeter, and a cryogenic thermometer. Together these instruments can form a complete thermal and radiation profile of the atmosphere throughout the flight. The students plan to pay special attention to data collected at aviation altitudes to learn how much radiation air travelers absorb during periods of high solar activity. Solar flare alerts: text, voice.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Realtime Venus Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Jan. 14, 2014, the network reported 12 fireballs.
(12 sporadics)
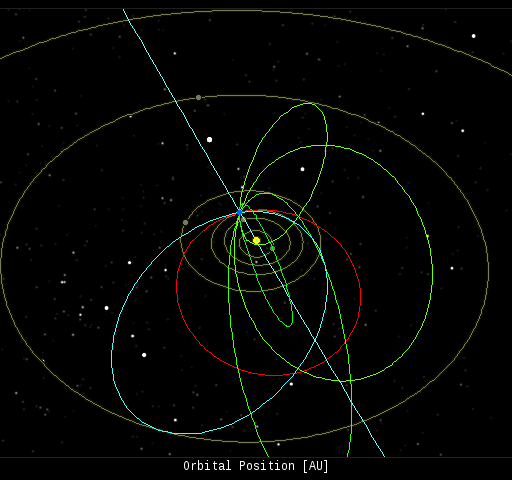
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On January 14, 2014 there were potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

