Metallic photos of the sun by renowned photographer Greg Piepol bring together the best of art and science. Buy one or a whole set. They make a stellar gift. | | |
RADIATION STORM IN PROGRESS: Solar protons accelerated by this morning's M9-class solar flare are streaming past Earth. On the NOAA scale of radiation storms, this one ranks S3, which means it could, e.g., cause isolated reboots of computers onboard Earth-orbiting satellites and interfere with polar radio communications. An example of satellite effects: The "snow" in this SOHO coronagraph movie is caused by protons hitting the observatory's onboard camera.
ALMOST-X FLARE AND CME (UPDATED): This morning, Jan. 23rd around 0359 UT, big sunspot 1402 erupted, producing a long-duration M9-class solar flare. The explosion's M9-ranking puts it on the threshold of being an X-flare, the most powerful kind. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured the flare's extreme ultraviolet flash:

The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and NASA's STEREO-B spacecraft detected a CME rapidly emerging from the blast site: movie. Analysts at the Goddard Space Weather Lab say the leading edge of the CME will reach Earth on Jan. 24 at 14:18UT (+/- 7 hours). Their animated forecast track shows that Mars is in the line of fire, too; the CME will hit the Red Planet during the late hours of Jan. 25.
This is a relatively substantial and fast-moving (2200 km/s) CME. Spacecraft in geosynchronous, polar and other orbits passing through Earth's ring current and auroral regions could be affected by the cloud's arrival. In addition, strong geomagnetic storms are possible, so high-latitude sky watchers should be alert for auroras. Magnetic storm alerts: text, voice.
JAN. 22ND CME IMPACT: Arriving a little later than expected, a coronal mass ejection (CME) hit Earth's magnetic field at 0617 UT on Jan. 22nd. According to analysts at the Goddard Space Weather Lab, the CME strongly compressed Earth's magnetic field and briefly exposed satellites in geosynchronous orbit to solar wind plasma. For the next 24 hours, Earth's magnetic field reverberated from the impact, stirring bright auroras around the Arctic Circle. Bjørn Jørgensen observed this display from Tromsø, Norway:

"This was amazing," he says. "It was a wonderful experience to see these stunning auroras."
NOAA forecasters estimate a 10% - 25% chance of continued geomagnetic storms tonight as effects from the CME impact subside. The odds will increase again on Jan. 24-25 as a new CME (from today's M9-clare) approaches Earth. High-latitude sky watchers should remain alert for auroras. Aurora alerts: text, voice.
UPDATED: January 2012 Aurora Gallery
[previous Januaries: 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, 2005, 2004]
The Jan. 22nd CME also disturbed Earth's ionosphere. In Atlanta, Georgia, radio engineer Pieter Ibelings monitored a 4.5 MHz CODAR (coastal radar) signal as it bounced off layers of ionization along the US east coast. "The moment of impact can be clearly seen on the CODAR radar plot," he points out:
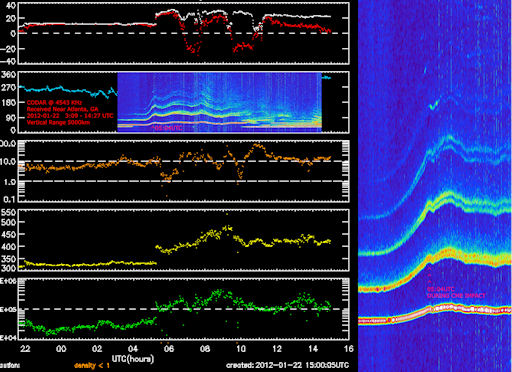
"The CODAR transmitters are located all around the coast and are used for mapping the ocean currents to a distance of about 200 miles," Ibelings explains. "These signals also propagate through the ionosphere so they can be picked up all around the world. The signals are almost perfect for ionospheric sounding since they are linear chirps. I capture the chirp with a receiver locked to GPS both in frequency and time. I then de-chirp the waveform so I can extract the time of arrival information at my location."
The CODAR echoes show ionization layers shifting vertical position by some hundreds of kilometers, changes that surely affected the propagation of HF radio signals in the aftermath of the impact. More information about Ibelings' observations may be found here.
Comet Lovejoy Gallery
[previous comets: McNaught, Holmes, Lulin, Tuttle, Ikeya-Zhang]

