Listen to radar echoes from satellites and meteors, live on listener-supported Space Weather Radio. | | |
X-FLARE! Long-lived sunspot AR1967 returned to the Earthside of the sun on Feb. 25th and promptly erupted, producing an X4.9-class solar flare. This is the strongest flare of the year so far and one of the strongest of the current solar cycle. A movie from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory shows the explosion hurling a loop of hot plasma away from the blast site:
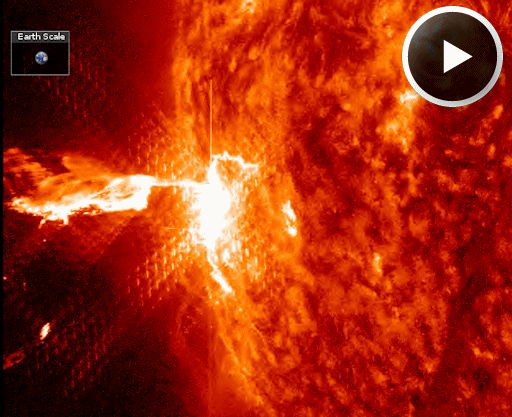
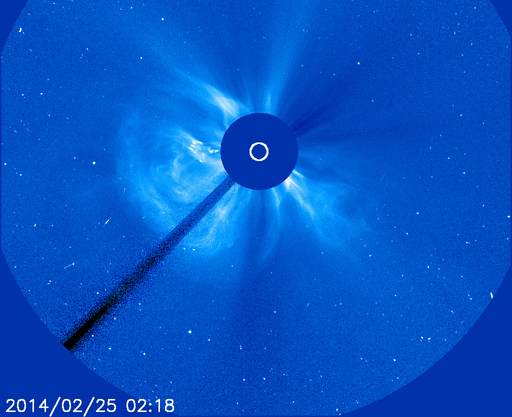
Coronagraphs onboard the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory tracked this material as it raced away from the sun, eventually forming a bright CME, pictured below.. Radio emissions from shock waves at the leading edge of the CME suggest an expansion velocity near 2000 km/s or 4.4 million mph. If such a fast-moving cloud did strike Earth, the resulting geomagnetic storms could be severe. However, because its trajectory is so far off the sun-Earth line, the CME will deliver a no more than a glancing blow. NOAA forecasters expect a weak impact late in the day on Feb. 26th.
The source of the eruption is long-lived sunspot AR1967, now beginning its third trip across the Earthside of the sun. This region was an active producer of flares during its previous transits, and it looks like the third time will be no different. By tradition, sunspots are renumbered each time they return, so AR1967 has been given a new name, AR1990. After today, that is what we will call it. Solar flare alerts: text, voice
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
MYSTERY CLOUD (DE-MYSTIFIED): On the night of Feb. 20/21, photographer Dennis Mammana was stationed on Pedro Dome near Fairbanks, Alaska, in hopes of recording the Northern Lights. "I caught this instead—a tiny and bright cloud that rose from the western sky and spread slightly and faded over an hour or so," says Mammana. Here is a composite of two of his shots:

The cloud resembles a rocket fuel dump. Scientists from the University of Alaska frequently launch rockets from the nearby Poker Flat Research Range to study auroras. But on this night there were no rocket launches on Poker Flat.
Update: There was, however, a launch thousands of miles away. A Delta 4 rocket blasted off from Cape Canaveral carrying a GPS satellite.
Veteran satellite watcher Marco Langbroek of the Netherlands says this is it: "The mystery object on the Mammana photo is a fuel vent from the Feb 20 launch of GPS 2F-05 (USA 248, 20114-008A, #39533)."
"Although the satellite is in an orbit with a 54.98 degree inclination, that does not mean it was not visible from Mammana's location at 65N," he continues. "It is in a very high orbit and was at an altitude of over 20,000 km at the time of the photo. At such an altitude it is visible from 65 N, low in the west in this case."
A sky map prepared by Langbroek shows the position of the satellite (labeled "Object A") in the sky above Alaska when Mammana saw the cloud. The sky map and the photo are a good match.
Update #2: Another sighting of the cloud has been reported, by David Cartier, Sr. located 30 km. east of Whitehorse, Yukon, Canada. Click here to see his photo.
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Feb. 25, 2014, the network reported 4 fireballs.
(4 sporadics)
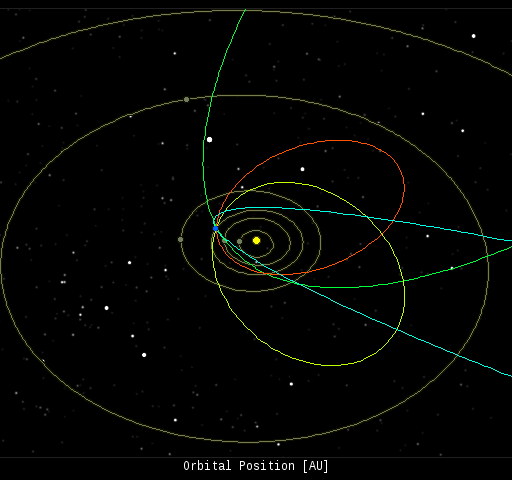
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On February 25, 2014 there were 1458 potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

