Lights Over Lapland is excited to announce that our Customizable Aurora Adventures are available for immediate booking! Reserve your adventure of a lifetime in Abisko National Park, Sweden today! | | |
LONG-RANGE FORECAST: NOAA forecasters say that G2-class geomagnetic storms are possible on Nov. 9-10 when a relatively potent stream of solar wind reaches Earth. A last-quarter Moon should provide dark enough skies for easy visibility of Arctic auroras. Free: Aurora Alerts.
RUSSIAN WAR GAMES SPARK 'BLUE AURORAS': Around the Arctic Circle, people see green auroras almost every night. It's nothing to write home about. Blue auroras, on the other hand, are very unusual. That's why this photo taken on Oct. 26th by Oliver Wright in Abisko, Sweden, is so remarkable:

"It was totally blue," says Wright, a veteran aurora tour guide who has witnessed hundreds of geomagnetic storms. "I've never seen anything quite like it!" In Tromso, Norway, Daniel Drelciuc saw it, too--"a big blue mass next to the classic green aurora," he says.
In auroras, blue is a sign of nitrogen. Energetic particles striking ionized molecular nitrogen (N2+) at very high altitudes can produce a cold azure glow, most often seen during intense geomagnetic storms. On Oct. 26th, however, geomagnetic activity was not intense.
Maybe these weren't auroras, after all. Another theory is emerging for the blue apparition. On Oct. 26th, the Russian military staged a nuclear battle drill and test-launched a number of ballistic missiles from land, sea and air. At least one of them created a magnificent cloud of blue exhaust. Alexey Yakovlev photographed the display from Strezhevoy, Russia:

His photo looks so strange, you might think it is Photoshopped. It's real. A sequence of images on Yakovlev's Russian language social media page shows the cloud expanding naturally into the atmosphere.
The instigating missile may have been a Topol ICBM reportedly launched from the Plesetsk space center 800 km north of Moscow toward the Kura test range in Kamchatka. The flight path is about right for a sighting by Yakovlev. Moreover, when Russia test-launched the same type of missile last month, some sky watchers reported unusual clouds then, too.
Perhaps high altitude winds blew some of this blue exhaust west, visually mixing with geomagnetic auroras over Scandinavia. Wright notes that the blue and green lights were indeed moving independently, as if they came from different sources. "I'm leaning toward the rocket explanation," he says.
Stay tuned for updates as more information becomes available.
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
OPALITE CRYSTAL SPACE PENDANT: On Oct. 15, 2017, the students Earth to Sky Calculus launched a space weather balloon from the Sierra Nevada mountains of central California. Its mission: to measure cosmic rays at the top of Earth's atmosphere. The payload carried an array of X-ray/gamma-ray detectors, GPS trackers, temperature/pressure sensors and, for fundraising, opalite crystals:
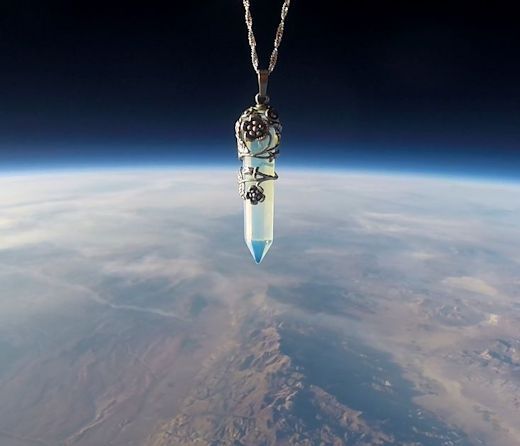

With a soothing blue glow that matches the otherworldly color of Earth's upper atmosphere, these crystals ascended to an altitude of 32 km (105,000 feet) where the balloon exploded. The payload parachuted back to Earth, landing in the Eureka Valley on the outskirts of Death Valley National Park.
You can have one for $119.95. Each necklace comes with a unique gift card showing the pendant floating at the top of Earth's atmosphere. The interior of the card tells the story of the flight and confirms that this gift has been to the edge of space and back again.
Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All proceeds support hands-on STEM education
(UPDATED MOVIE) UNUSUAL COMET DIVES TOWARD THE SUN: Deep inside the orbit of Mercury, unusual comet 96P/Machholz is diving toward the sun today. At closest approach on Oct. 27th, it will swoop through the sun's gravity well just 0.12 AU from the star. Coronagraphs onboard the orbiting Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) are monitoring the flyby:
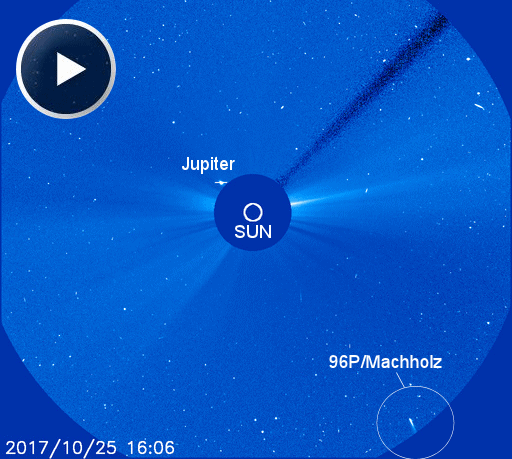
Comet 96P does this every 5.24 years. It is a short period comet that experiences frequent blasts of solar heat. During a similar flyby in 2002, SOHO observed two tiny fragments ahead of the main nucleus. This means the comet may be actively evolving, and it could shed more pieces during this week's dive.
This is no ordinary comet. Its orbit connects it with a bewildering menagerie of other things in the solar system: Comet 96P is linked to as many as three meteor showers (the Daytime Arietids, Southern Delta Aquarids, and Quadrantids), two families of sungrazing comets, and an asteroid (2003 EH1). Millennia ago, the whole ensemble was probably part of the same parent object that exploded or fell apart.
Does this comet even belong to our own solar system? A scientific study published in 2008 found that 96P/Machholz has "extremely anomalous molecular abundances." Chemically speaking, it's not like other comets that have been studied in the same way. Perhaps it comes from another star system, flung into space and later captured by our own sun's gravity.
96P/Machholz will remain visible in SOHO coronagraphs from now until Oct. 30th. Check back often for updated images.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of
NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Oct. 28, 2017, the network reported 50 fireballs.
(34 sporadics, 10 Orionids, 4 Southern Taurids, 2 epsilon Geminids)
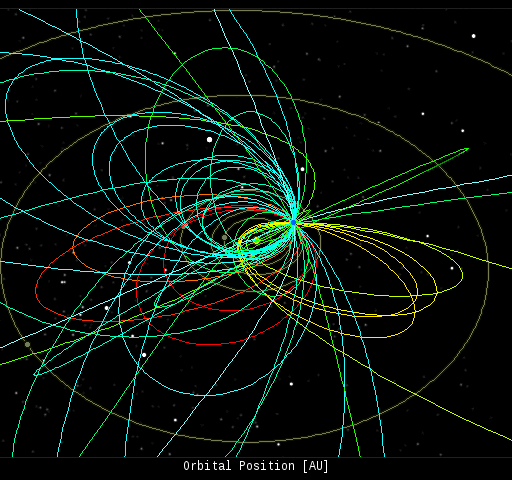
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On October 28, 2017 there were 1849 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 |
Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) |
| 2017 TK6 | 2017-Oct-23 | 19.3 LD | 11.7 | 45 |
| 2017 UU2 | 2017-Oct-24 | 2.1 LD | 11.3 | 19 |
| 2017 UK3 | 2017-Oct-24 | 1.4 LD | 13.3 | 13 |
| 2017 UP5 | 2017-Oct-24 | 6.5 LD | 10.2 | 10 |
| 2017 UH | 2017-Oct-25 | 15.1 LD | 11 | 21 |
| 2017 UE3 | 2017-Oct-25 | 4.7 LD | 15.1 | 29 |
| 2017 UG6 | 2017-Oct-25 | 14 LD | 6.9 | 33 |
| 2017 UG3 | 2017-Oct-25 | 12.4 LD | 5.3 | 13 |
| 2017 TL4 | 2017-Oct-25 | 14.7 LD | 11.4 | 49 |
| 2017 UJ5 | 2017-Oct-26 | 18.8 LD | 6.3 | 42 |
| 2017 UM5 | 2017-Oct-27 | 6 LD | 17.1 | 27 |
| 2017 UB6 | 2017-Oct-28 | 12.4 LD | 7.5 | 13 |
| 2017 UK6 | 2017-Oct-28 | 11.9 LD | 14.8 | 61 |
| 2017 UL6 | 2017-Oct-28 | 0.2 LD | 8 | 1 |
| 2017 UA6 | 2017-Oct-29 | 4 LD | 15 | 26 |
| 2017 UJ6 | 2017-Oct-30 | 5.5 LD | 11.3 | 18 |
| 2017 TZ4 | 2017-Oct-31 | 19.3 LD | 13.1 | 96 |
| 2003 UV11 | 2017-Oct-31 | 15 LD | 24.5 | 447 |
| 2017 UP6 | 2017-Oct-31 | 15.1 LD | 11.6 | 22 |
| 2017 UO2 | 2017-Oct-31 | 11 LD | 8.7 | 22 |
| 2013 BD74 | 2017-Nov-06 | 10.6 LD | 9 | 51 |
| 2017 TZ3 | 2017-Nov-09 | 10.3 LD | 8.7 | 39 |
| 444584 | 2017-Nov-17 | 8.7 LD | 14.8 | 324 |
| 2008 WM61 | 2017-Dec-03 | 3.8 LD | 4.7 | 16 |
| 2015 XX169 | 2017-Dec-14 | 9.7 LD | 6.3 | 11 |
| 2011 YD29 | 2017-Dec-19 | 17.6 LD | 7.7 | 20 |
| 2006 XY | 2017-Dec-20 | 6.5 LD | 5 | 56 |
| 418849 | 2017-Dec-22 | 15.3 LD | 17.4 | 257 |
| 2017 TS3 | 2017-Dec-22 | 18.2 LD | 10.3 | 136 |
| 2015 YQ1 | 2017-Dec-22 | 17.3 LD | 11.1 | 9 |
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
Readers, thank you for your patience while we continue to develop this new section of Spaceweather.com. We've been working to streamline our data reduction, allowing us to post results from balloon flights much more rapidly, and we have developed a new data product, shown here:
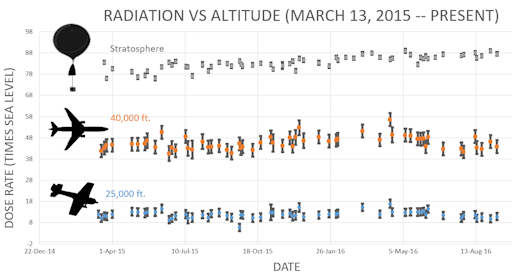
This plot displays radiation measurements not only in the stratosphere, but also at aviation altitudes. Dose rates are expessed as multiples of sea level. For instance, we see that boarding a plane that flies at 25,000 feet exposes passengers to dose rates ~10x higher than sea level. At 40,000 feet, the multiplier is closer to 50x. These measurements are made by our usual cosmic ray payload as it passes through aviation altitudes en route to the stratosphere over California.
What is this all about? Approximately once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with radiation sensors that detect cosmic rays, a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. Cosmic rays can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Furthermore, there are studies ( #1, #2, #3, #4) linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the general population. Our latest measurements show that cosmic rays are intensifying, with an increase of more than 13% since 2015:
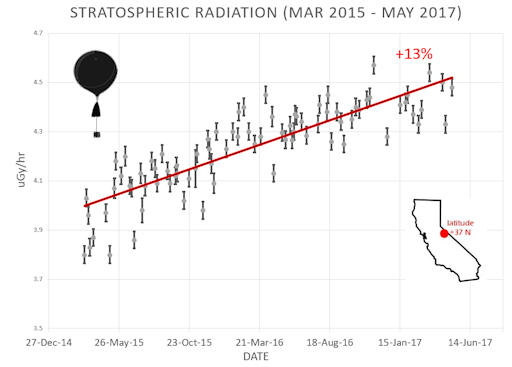
Why are cosmic rays intensifying? The main reason is the sun. Solar storm clouds such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays when they pass by Earth. During Solar Maximum, CMEs are abundant and cosmic rays are held at bay. Now, however, the solar cycle is swinging toward Solar Minimum, allowing cosmic rays to return. Another reason could be the weakening of Earth's magnetic field, which helps protect us from deep-space radiation.
The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
The data points in the graph above correspond to the peak of the Reneger-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Reneger and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today.
| | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |
 | Reviews here can help you to pick up best memory foam mattresses. |
| | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! |
| | | | | | |

