AURORA ALERTS: Did you miss the Northern Lights? Next time get a wake-up call from Space Weather PHONE | | |
 |
LONG-DELAY RADIO ECHOES: During the geomagnetic storm of Nov. 27th, a brief but intense G2-class event, amateur radio operator Peter Brogl of Fürth, Germany, experienced a strange phenomenon. Forty-six seconds after he transmitted his call sign at 7 MHz, he received an echo of his own transmission. "At first, I thought someone was playing tricks on me," says Brogl, "but I changed frequency, re-keyed my call sign (DK6NP), and got another echo." This went on for more than an hour, enough time for Brogl to make several recordings. First reported in 1927 by Norwegian civil engineer Jørgen Hals, long-delay radio echoes are rare and poorly understood. Unusual propagation conditions linked to solar storms is one of many possible explanations. Radio operators, if you experienced any similar phenomena on Nov. 27th between 1800 UT and 19:30 UT, please report your observations to Peter Brogl for correlation.
SUNSPOT CANOPY: Two days ago, sunspot 1130 didn't exist. Now the fast-growing sunspot group is the largest visible feature on the sun's disk with twin cores both larger than Earth. The amazing thing, however, is the invisible part. Using extreme ultraviolet filters outside the range of human vision, NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory took this picture of the sunspot's magnetic canopy on Nov. 30th:

In the image, curvaceous lines of magnetism are illuminated by hot solar plasma trapped inside the canopy. If the magnetic field becomes unstable and explodes, as sunspot magnetic fields often do, a cloud of plasma could come flying toward Earth. This active region merits watching for the next few days until the sun's rotation turns it away from our planet. Stay tuned.
RETURN OF JUPITER'S MISSING STRIPE: The revival of Jupiter's South Equatorial Belt (SEB), missing for nearly a year, is now well underway. The roiling, turbulent disturbance that heralds the brown stripe's full return stretches almost halfway around the giant planet. "Here is a projection map showing the revival on Nov. 29th," says amateur astronomer Wayne Jaeschke of West Chester, Pennsylvania. Note the region bracketed by arrows:
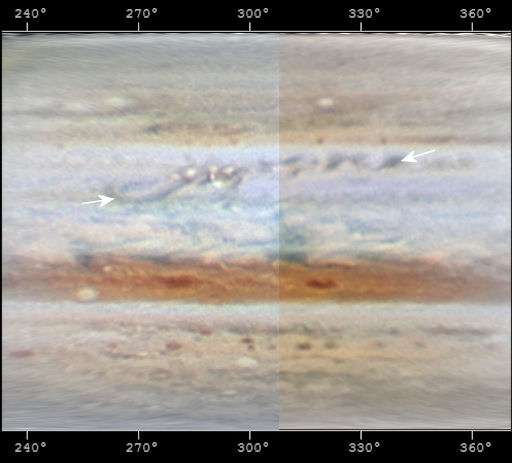
"I made the map by combining two pictures of Jupiter I took using my 14-inch Celestron telescope," says Jaeschke. "The disturbance has grown dramatically since it first appeared in late October." Indeed, it is now so large that even novice observers are starting to notice it in the eyepieces of backyard telescopes.
The spreading disturbance is not the SEB itself. Instead, it is thought to be a progressive clearing of high clouds that will eventually reveal the brown stripe hiding below. When the SEB finally returns, Jupiter will have two brown stripes again and the planet's appearance will return to normal. Meanwhile, amateur astronomers are encouraged to monitor the revival. Point your optics south after sunset: sky map.
more images: from Wayne Jaeschke of West Chester, PA; from Geoff Chester of Alexandria, Virginia; from John Nassr of Baguio, Philippines
November 2010 Aurora Gallery
[previous Novembers: 2009, 2008, 2007, 2006, 2004, 2003, 2002, 2001, 2000]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On November 30, 2010 there were 1164 potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

