Never miss another geomagnetic storm. Sign up for Space Weather Alerts and you'll receive a text message when magnetic storms erupt. Aurora tour guides and professional astronomers use this service. You can, too! | | |
A DANGEROUS SUNSPOT: Sunspot AR3089 has been quiet for days. Could it be the calm before the storm? The sunspot has developed a delta-class magnetic field that harbors energy for X-class solar flares. If there is such an eruption (NOAA estimates a 5% chance) it will be geoeffective because the sunspot is almost directly facing Earth. Solar flare alerts: SMS Text
DUNG BEETLES NAVIGATE USING THE MILKY WAY: When you hear the words "dung beetle" you probably think of poop. After you read this article, a different picture may come to mind: The Milky Way.
In 2009, entomologists made an astonishing discovery. Nocturnal dung beetles (Scarabaeus satyrus) can navigate using the Milky Way. Although the compound eyes of beetles cannot resolve individual stars, this species can see the Milky Way as a stripe across the sky and perhaps even sense features within it such as the galactic center and lanes of stardust.

Above: A nocturnal dung beetle at work. Photo credit: Chris Collingridge © 2017
"Currently, dung beetles are the only animals we know of that use the Milky Way for reliable orientation," says James Foster of the University of Konstanz in Germany. "They are excellent little astronomers."
A quick review of dung beetles: They are nature's sanitation crew. Whenever a pile of brown material is dumped in the forest, dung beetles converge to clean up the mess. Each beetle sculpts a dung ball, which they roll away in a straight line. Far from the pile, the ball will be buried and eaten, and sometimes used as bedding for dung beetle eggs.
It sounds simple, but there's a problem. Dung beetles are combative. If two beetles leaving the pile bump into one other, they can get into a brutal wrestling match often ending with overhead judo-style full body throws. Wandering around in circles (like lost humans do) boosts the odds of a fight even more. Dung beetles have therefore evolved the ability to navigate to safety in quick straight lines.
During the day they steer by the sun. Dung beetles can see polarization patterns in the daytime sky, and use these patterns to hold course. A single patch of blue sky is sufficient. The trick works at night, too. Dung beetles are the only known creatures who can see the polarization of moonlight, which is 100 million times weaker than daylight polarization. Studies show that dung beetles walk straight as accurately at night as during the day, even when the Moon is a faint crescent.
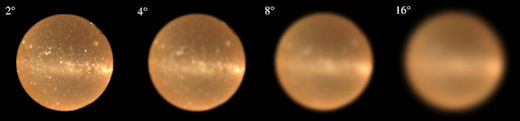
Above: Dung beetle vision blurs the Milky Way, but no one is certain how much. These are four models used in the experiments of James Foster.
But what happens when there's no sun or Moon? In the early 2000s, this question troubled two pioneers of dung beetle research, Eric Warrant and Marie Dacke of Lund University in Sweden. To find the answer, they took some beetles to the planetarium at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa, and projected the Milky Way onto the domed ceiling. The beetles saw it, and navigated.
Their discovery prompted a veritable explosion in dung beetle research. James Foster is a leader in the field, publishing new results every few years.
Foster and colleagues have built a rudimentary planetarium just for dung beetles. It uses LED lights to mimic the Milky Way as beetles see it through their compound eyes. In 2017 they found that dung beetles were able to distinguish between north and south arms of the Milky Way, sensing intensity contrasts as low as 13%. This threshold puts features such as the galactic center in Sagittarius and the Great Rift in Cygnus theoretically within range of beetle senses.
Next they added city lights to their experiment--and the results were not good. "Light pollution may be forcing beetles to abandon the Milky Way as their compass," worries Foster.

Above: Researcher Claudia Tocco observes the behavior of a dung beetle surrounded by urban lights. Photo credit Marcus Byrne.
In a paper published July 2021, Foster's team described how urban lights wipe out the Milky Way, reduce the polarization of moonlight by 60% to 70%, and "create anthropogenic celestial cues." The last item is worst of all. Spotlights and brightly lit buildings mesmerize beetles who suddenly ignore the sky and make a beeline for manmade bulbs.
"These beacons draw beetles towards the most hostile regions of their environments," says Foster. "After rolling their balls some distance, beetles need to find a patch of soft sand where they can dig in. They are unlikely to find that in the immediate vicinity of bright artificial lights, whether in cities or the countryside, since these are usually associated with concrete and tarmac."
Dung beetles aren't the only ones. Researchers believe they are only scratching the surface of this field with potentially thousands of species watching the stars. Everything from simple light bulbs to sophisticated satellite megaconstellations may be affecting these members of our ecosystem.
"Dung beetle!" What are you thinking of now?
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
OCEAN BLUE CRYSTAL DOLPHIN PENDANT: Are you looking for a far-out gift? Consider the Ocean Blue Crystal Dolphin Pendant. It flew to the stratosphere on April 8th onboard a cosmic ray research balloon:

You can have it for $199.95. The students of Earth to Sky Calculus are selling these crystal cetaceans to support their cosmic ray monitoring program.
The dolphin is wrapped in a sterling silver wave and suspended from a matching 18-inch chain. It contains no nickel, no lead, no cadmium; the pendant is totally hypoallergenic. Each pendant comes with a greeting card showing the dolphin in flight, and telling the story of its trip to the edge of space and back again.
Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All sales support hands-on STEM education
Realtime Noctilucent Cloud Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Every night, a network of
NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Sep 01, 2022, the network reported 14 fireballs.
(11 sporadics, 3 alpha Aurigids)
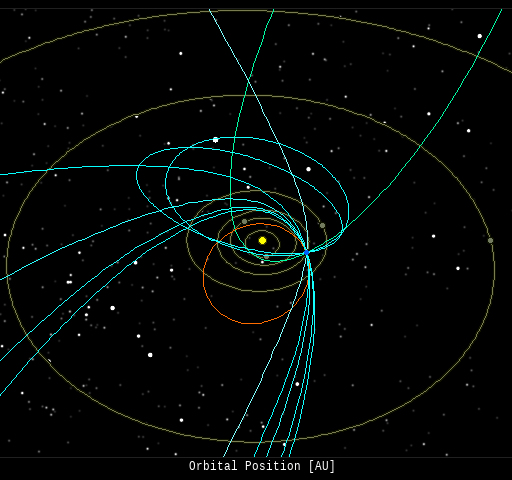
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On September 1, 2022 there were 2281 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 |
Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) |
| 2022 QP6 | 2022-Aug-27 | 2 LD | 13.6 | 14 |
| 2022 QQ4 | 2022-Aug-27 | 15.5 LD | 7.2 | 32 |
| 2022 QP31 | 2022-Aug-27 | 5.1 LD | 5.5 | 17 |
| 2022 QQ31 | 2022-Aug-28 | 1.7 LD | 14.8 | 9 |
| 2022 QP3 | 2022-Aug-28 | 14.4 LD | 7.9 | 30 |
| 2022 QX4 | 2022-Aug-29 | 4.8 LD | 8.8 | 41 |
| 2017 BU | 2022-Aug-29 | 15.8 LD | 7 | 32 |
| 2022 QX1 | 2022-Aug-31 | 5.4 LD | 21.1 | 41 |
| 2022 QB8 | 2022-Aug-31 | 18.9 LD | 10.6 | 23 |
| 2022 QZ6 | 2022-Aug-31 | 3.3 LD | 11.2 | 36 |
| 2022 QS7 | 2022-Aug-31 | 13.1 LD | 7.7 | 21 |
| 2022 QT7 | 2022-Sep-01 | 1.2 LD | 7.7 | 6 |
| 2021 CQ5 | 2022-Sep-01 | 8.7 LD | 13.5 | 7 |
| 2022 QB2 | 2022-Sep-01 | 10.3 LD | 15.9 | 33 |
| 2022 QN5 | 2022-Sep-02 | 2.4 LD | 13.5 | 22 |
| 2022 QO31 | 2022-Sep-03 | 14 LD | 8.5 | 47 |
| 2022 QJ7 | 2022-Sep-05 | 14.8 LD | 12 | 26 |
| 2022 QU5 | 2022-Sep-05 | 19.2 LD | 7.1 | 31 |
| 2022 QC7 | 2022-Sep-06 | 12.2 LD | 9.1 | 22 |
| 2022 QR31 | 2022-Sep-06 | 19.9 LD | 11.3 | 54 |
| 2022 QB22 | 2022-Sep-09 | 14.2 LD | 17.5 | 57 |
| 2022 QF2 | 2022-Sep-11 | 19.1 LD | 8.4 | 44 |
| 2008 RW | 2022-Sep-12 | 17.5 LD | 10.2 | 98 |
| 2020 PT4 | 2022-Sep-15 | 18.8 LD | 10.8 | 39 |
| 2022 QD1 | 2022-Sep-16 | 19.4 LD | 9.5 | 72 |
| 2022 QH8 | 2022-Sep-22 | 10.6 LD | 15.3 | 55 |
| 2016 HF2 | 2022-Sep-29 | 19.2 LD | 5.6 | 21 |
| 2018 ER1 | 2022-Oct-02 | 14.7 LD | 4 | 27 |
| 2018 VG | 2022-Oct-05 | 18.5 LD | 6.7 | 12 |
| 2021 TJ10 | 2022-Oct-06 | 19.6 LD | 8.1 | 6 |
| 2006 SG7 | 2022-Oct-07 | 16.7 LD | 18.4 | 93 |
| 2013 TJ6 | 2022-Oct-07 | 11.7 LD | 14.4 | 32 |
| 2013 SL20 | 2022-Oct-14 | 6.2 LD | 12.1 | 45 |
| 2020 TO2 | 2022-Oct-15 | 1.4 LD | 12.6 | 18 |
| 2020 BD | 2022-Oct-16 | 12.1 LD | 11.4 | 20 |
| 2022 QM6 | 2022-Oct-17 | 19.8 LD | 4.2 | 69 |
| 2016 TH94 | 2022-Oct-25 | 19.1 LD | 13.5 | 43 |
| 2019 AN5 | 2022-Oct-27 | 20 LD | 6.8 | 213 |
| 2004 UT1 | 2022-Oct-29 | 4 LD | 6.3 | 17 |
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
SPACE WEATHER BALLOON DATA: Almost once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with sensors that detect secondary cosmic rays, a form of radiation from space that can penetrate all the way down to Earth's surface. Our monitoring program has been underway without interruption for 7 years, resulting in a unique dataset of in situ atmospheric measurements.
Latest results (July 2022): Atmospheric radiation is decreasing in 2022. Our latest measurements in July 2022 registered a 6-year low:
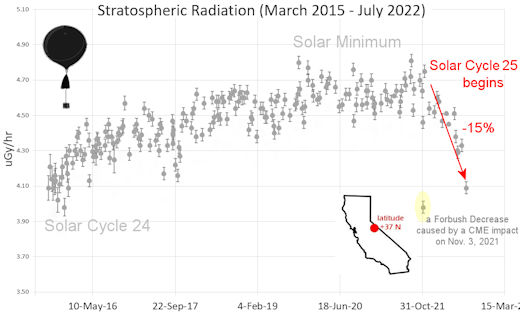
What's going on? Ironically, the radiation drop is caused by increasing solar activity. Solar Cycle 25 has roared to life faster than forecasters expected. The sun's strengthening and increasingly tangled magnetic field repels cosmic rays from deep space. In addition, solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays, causing sharp reductions called "Forbush Decreases." The two effects blend together to bring daily radiation levels down.
.Who cares? Cosmic rays are a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. They can alter the chemistry of the atmosphere, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. According to a study from the Harvard T.H. Chan school of public health, crews of aircraft have higher rates of cancer than the general population. The researchers listed cosmic rays, irregular sleep habits, and chemical contaminants as leading risk factors. A number of controversial studies (#1, #2, #3, #4) go even further, linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
Technical notes: The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
Data points in the graph labeled "Stratospheric Radiation" correspond to the peak of the Regener-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Regener and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today.
| | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | information about sunspots based on the latest NOAA/USAF Active Region Summary |
| | current counts of failed and deployed Starlink satellites from Jonathan's Space Page |
| | Authoritative predictions of space junk and satellite re-entries |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |
 | BestCSGOGambling is the best site for everything related to CSGO gambling on the web |
 | To find reviews of new online casino sites in the UK try The Casino DB where there are hundreds of online casino reviews complete with bonuses and ratings. Alternatively, Online-Casinos.xyz is another massive directory of online casinos listing sites for the UK and Worldwide. Casinos that offer Rupees for bonuses are very generous to Indian players. Find the best online casinos in India at AllCasinos.in Looking for a new online casino? Try Casimpo the new site dedicated to making online casino simple, or check out the new Avenger Slots Casino and Ace Online Casino with over 500 online slots and casino games. |
 | One of the most popular casino games is the Book Of Dead Slot based on ancient Egyptian text, you can find all the casinos with spins at bookofdeadslotsites.com. |
 | When looking for casinos to play online when the weather is bad, you can try casino online trucchi for Italian games. If you are not from Finland you can try the Swedish page Svenska casino online to find suitable games, check out svenskacasinoonline.net. Always check your local laws before playing with real money. |
 | Looking for sports betting companies not registered on GamStop? CasinoGap has presented a list of sites not on GamStop available for UK players. Check and bet online! Would you like to bet at sites not using GamStop? Look at a list of NonStopCasino sites for online betting that aren't on GamStop. Top-rated bookmakers ever! |
| | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! |
| | | | | | |

