 | | | Switch to: Europe, USA, New Zealand, Antarctica Credit: NOAA/Ovation  Planetary K-index Planetary K-index
Now: Kp= 2.67 quiet
24-hr max: Kp= 3.33 quiet
explanation | more data
Interplanetary Mag. Field
Btotal: 4.16 nT
Bz: 2.49 nT north
more data: ACE, DSCOVR
Updated: Today at 1151 UT  Coronal Holes: 23 Jun 24 Coronal Holes: 23 Jun 24 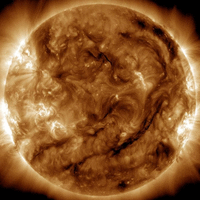
There are no equatorial coronal holes on the Earthside of the sun.Credit: SDO/AIA  Polar Stratospheric Clouds
Colorful Type II polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) form when the temperature in the stratosphere drops to a staggeringly low -85C. NASA's MERRA-2 climate model predicts when the air up there is cold enough: 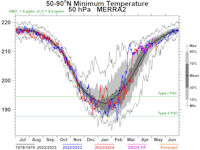
On June 23, 2024, the Arctic stratosphere is much too warm for Type II polar stratospheric clouds. | more data. Noctilucent Clouds
They're back! The northern season for NLCs is underway. The first clouds were detected inside the Arctic Circle on May 25, 2024, by the NOAA 21 satellite. The clouds have since spread, and now observers are seeing from the ground as well:
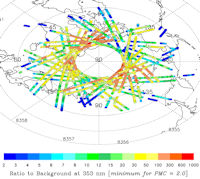
Updated: June 21, 2024
An instrument onboard NOAA 21 (OMPS LP) is able to detect NLCs (also known as "polar mesospheric clouds" or PMCs). IN the daily map, above, each dot is a detected cloud. As the season progresses, these dots will multiply in number and shift in hue from blue to red as the brightness of the clouds intensifies.
 SPACE WEATHER
NOAA Forecasts | | Updated at: 2024 Jun 23 2200 UTC FLARE | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | CLASS M | 60 % | 60 % | CLASS X | 15 % | 15 % |  Geomagnetic Storms: Geomagnetic Storms:
Probabilities for significant disturbances in Earth's magnetic field are given for three activity levels: active, minor storm, severe storm Updated at: 2024 Jun 23 2200 UTC Mid-latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 15 % | 10 % | MINOR | 05 % | 01 % | SEVERE | 01 % | 01 % | High latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 15 % | 15 % | MINOR | 25 % | 20 % | SEVERE | 25 % | 20 % | | | |  | | | | | | | | | | | This is an AI Free Zone! Text created by Large Language Models is spreading rapidly across the Internet. It's well-written, artificial, frequently inaccurate. If you find a mistake on Spaceweather.com, rest assured it was made by a real human being. | | | MARTIAN AURORA WARNING: A CME is heading for Mars. According to a NASA model, the storm cloud will strike the Red Planet on June 27th. The impact could spark global auroras and erode a small amount of the planet's atmosphere. Aurora alerts: SMS Text SOMETHING FLARE-Y THIS WAY COMES: Old sunspot AR3664 might not be dead, after all. It's returning today for a rare third trip across the Earthside of the sun. Usually such a superannuated sunspot would be a decaying corpse. Instead, we're getting an explosive active region: 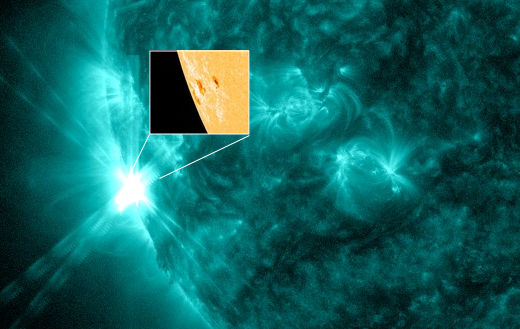
An M9.7-class solar flare on June 23, 2024, with the underlying sunspot inset.
Earlier today, the returning sunspot unleashed an M9.3-class solar flare, only percentage points away from category X. The sunspot itself is only a fraction of its former size, but something about its magnetic underpinnings continues to produce strong flares. Stay tuned for more. Solar flare alerts: SMS Text Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter BUSY INTERSECTION: German astronomer Achim Schaller was watching the sun on June 18, 2024, when several things happened at once. His camera clicked, a plane flew overhead, smearing its contrail across the field of view, and the International Space Station (ISS) split the gap between two giant sunspots. It was one busy intersection: 
"Traveling at 17,000 mph, the ISS took less than 2 seconds to cross the solar disk," says Schaller. "In that time I managed to take 17 pictures." The ISS isn't the only spaceship transiting sunspots. On June 15th, Philip Smith watched an unidentified flying object cross AR3712 over Manorville, NY. "I am not saying this UFO was a flying saucer," says Smith. "It's probably just an Earth-orbiting satellite, but I don't know which one." (Neither do we, but it's a great movie.) Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
COLLECTABLE STAR TREK ORNAMENT: No Trekkie Christmas tree is complete without The Arena Ornament. This rare Hallmark keepsake depicts the reptilian Gorn poised to deliver a death blow to Capt. James T. Kirk on the planet Cestus III. On June 14, 2024, it flew to the edge of space onboard a cosmic ray research balloon: 
You can have it for $135.95. The ornament depicts a famous scene from The Original Series episode "Arena" first broadcast on January 19, 1967. Decades later, the Gorn have become main villians on the new Star Trek series Strange New Worlds, which we love! The ornament comes with a Christmas card showing Kirk and the Gorn in flight, and certifying they have traveled to the edge of space and back again.
Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All sales support hands-on STEM education
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Realtime Noctilucent Cloud Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Jun 22, 2024, the network reported 4 fireballs.
(4 sporadics) 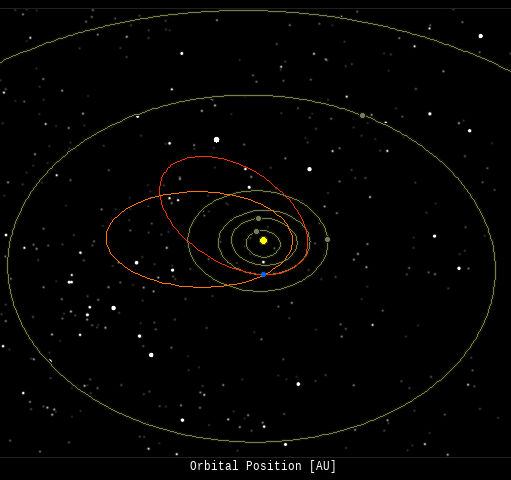 In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On June 23, 2024 there were 2349 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 | Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) | | 2024 MA | 2024-Jun-18 | 4.2 LD | 11.2 | 17 | | 2024 KY1 | 2024-Jun-19 | 16.1 LD | 12.2 | 36 | | 2024 MC | 2024-Jun-19 | 6.5 LD | 14.3 | 56 | | 2024 LO3 | 2024-Jun-20 | 1.9 LD | 8 | 22 | | 2024 LG5 | 2024-Jun-21 | 6.1 LD | 7.5 | 17 | | 2024 LO2 | 2024-Jun-21 | 14.2 LD | 9.1 | 28 | | 2024 LJ | 2024-Jun-22 | 8.8 LD | 18.5 | 66 | | 2024 KN1 | 2024-Jun-23 | 14.7 LD | 4.6 | 28 | | 2024 KJ | 2024-Jun-25 | 13.7 LD | 4.5 | 25 | | 2024 LO5 | 2024-Jun-25 | 5.1 LD | 7.9 | 20 | | 2019 NJ | 2024-Jun-27 | 17.2 LD | 10.1 | 66 | | 415029 | 2024-Jun-27 | 17.3 LD | 25.9 | 2304 | | 2022 MM1 | 2024-Jun-28 | 7.8 LD | 10.9 | 39 | | 2010 XN | 2024-Jun-28 | 14.1 LD | 11.3 | 52 | | 2022 HD1 | 2024-Jun-29 | 16.5 LD | 7.2 | 63 | | 2024 MK | 2024-Jun-29 | 0.8 LD | 9.4 | 158 | | 2017 MB3 | 2024-Jun-30 | 5 LD | 6.5 | 30 | | 2024 JJ25 | 2024-Jun-30 | 10.5 LD | 9.4 | 117 | | 2024 LJ2 | 2024-Jul-01 | 19.8 LD | 10.4 | 83 | | 2022 BY39 | 2024-Jul-02 | 13.2 LD | 3 | 4 | | 2024 LH | 2024-Jul-02 | 4.4 LD | 4.3 | 32 | | 2024 KQ1 | 2024-Jul-04 | 14.9 LD | 6.9 | 57 | | 2022 YS5 | 2024-Jul-11 | 11 LD | 5.8 | 38 | | 2024 BY15 | 2024-Jul-16 | 16.2 LD | 0.7 | 16 | | 2024 LY2 | 2024-Jul-23 | 12 LD | 7.8 | 88 | | 2011 MW1 | 2024-Jul-25 | 10.1 LD | 8 | 120 | | 2011 AM24 | 2024-Jul-26 | 16.8 LD | 6.2 | 281 | | 523664 | 2024-Jul-28 | 14.9 LD | 23.7 | 680 | | 2020 PN1 | 2024-Aug-02 | 18 LD | 5.5 | 29 | | 2023 HB7 | 2024-Aug-05 | 14.6 LD | 6.1 | 32 | | 2017 TU1 | 2024-Aug-05 | 10.1 LD | 10.1 | 22 | | 2024 KH3 | 2024-Aug-10 | 14.6 LD | 11.4 | 197 | | 2021 GY1 | 2024-Aug-16 | 17.7 LD | 6.3 | 59 | | 2024 JV33 | 2024-Aug-19 | 12 LD | 11.1 | 220 | | 2022 BF2 | 2024-Aug-19 | 19.7 LD | 16.4 | 91 | Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere | SPACE WEATHER BALLOON DATA: Almost once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with sensors that detect secondary cosmic rays, a form of radiation from space that can penetrate all the way down to Earth's surface. Our monitoring program has been underway without interruption for 7 years, resulting in a unique dataset of in situ atmospheric measurements. Latest results (July 2022): Atmospheric radiation is decreasing in 2022. Our latest measurements in July 2022 registered a 6-year low: 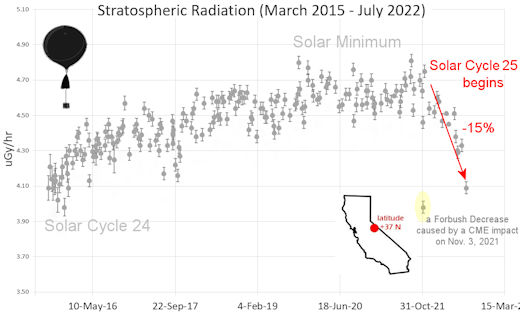
What's going on? Ironically, the radiation drop is caused by increasing solar activity. Solar Cycle 25 has roared to life faster than forecasters expected. The sun's strengthening and increasingly tangled magnetic field repels cosmic rays from deep space. In addition, solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays, causing sharp reductions called "Forbush Decreases." The two effects blend together to bring daily radiation levels down. .Who cares? Cosmic rays are a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. They can alter the chemistry of the atmosphere, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. According to a study from the Harvard T.H. Chan school of public health, crews of aircraft have higher rates of cancer than the general population. The researchers listed cosmic rays, irregular sleep habits, and chemical contaminants as leading risk factors. A number of controversial studies (#1, #2, #3, #4) go even further, linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Technical notes: The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners. Data points in the graph labeled "Stratospheric Radiation" correspond to the peak of the Regener-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Regener and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | information about sunspots based on the latest NOAA/USAF Active Region Summary | | | current counts of failed and deployed Starlink satellites from Jonathan's Space Page. See also, all satellite statistics. | | | Authoritative predictions of space junk and satellite re-entries | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather |  | Got a chipped or cracked windshield that prevents you from seeing space weather events while driving? Get windshield replacement from SR Windows & Glass with free mobile auto glass service anywhere in the Phoenix area. |  | Marketing yourself on YouTube is hard without real organic views on your videos. You can buy organic YouTube views from and enjoy social boosting that is actually real. Highly recommended! |  | BestCSGOGambling is the best site for everything related to CSGO gambling on the web | | | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! | | | | | | | | |  | |  |   | ©2021 Spaceweather.com. All rights reserved. This site is penned daily by Dr. Tony Phillips. | |

